Remember when success in education meant simply counting how many kids showed up to class? Those days are gone.
Now, it’s about real impact—especially in places that need it most.
Rural education faces unique challenges. The digital divide tells the story: a striking 23.8% gap exists between rural schools (where just 44.9% have digital infrastructure) and their urban counterparts (at 68.7%).
Not exactly a level playing field, is it?
Corporate Social Responsibility, or CSR in education, has evolved alongside this reality. Companies aren’t just writing checks for new buildings anymore—they’re asking the tough question: “Are students actually learning better?”
It’s a shift from the old “build it and they will come” approach to something smarter.
By mixing data-driven strategies, environmental and social goals, and getting all the stakeholders involved, CSR programmes are creating change you can actually measure.
Because, at the end of the day, isn’t that what matters?
Who are the Key Stakeholders in Education Impact Measurement?
The key stakeholders of the education impact ecosystem are:
1. Schools and Educators
Educational institutions, teachers, and administrators are instrumental in the successful implementation of educational programmes and their measurement.
They create environments and plan lessons to improve student performance and maintain school attendance levels.
2. CSR Departments
CSR departments plan, execute, and monitor education initiatives and allocate resources. They are also responsible for aligning the programmes with company values and stakeholder expectations.
3. Government Bodies
Government bodies specify the protocols and objectives of the education system. Local authorities and officials play a pivotal role in implementing policies effectively and timely intervention when required.
4. Implementation Partners
Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) and Civil Society Organisations (CSOs) collaborate with government bodies and educators to implement educational programmes that support marginalised communities.
Additionally, next-gen EdTech companies and platforms like iDream Education, with their smart classrooms, help empower education delivery, impact measurement, and personalised learning.
Traditional vs. Modern Impact Measurement Approaches to Education CSR
Traditional approaches focused on short-term outcomes are giving way to modern, data-driven mechanisms that focus on long-term qualitative improvements in the education system.
Here’s a quick comparison between the two approaches:
| Traditional Education CSR | Modern Education CSR |
| Focused on donations and infrastructure, physical amnesties, and resources. | Focused on learning outcomes and systemic change, like providing digital education access |
| Qualitative and activity-based measurement approach. | Quantitative, evidence-based, and tech-driven measurement approach. |
| Data collection is through manual reports | Use of AI, Big Data, and Real-Time Tracking for data collection. |
For example, Project Alankar, initiated by the Gorakhpur Development Authority in Uttar Pradesh, represents a significant advancement in technology integration within government schools.
It focuses on enhancing traditional smart classrooms by incorporating continuous usage reporting and data-driven monitoring to improve learning outcomes.
Challenges in Rural Education Data Collection
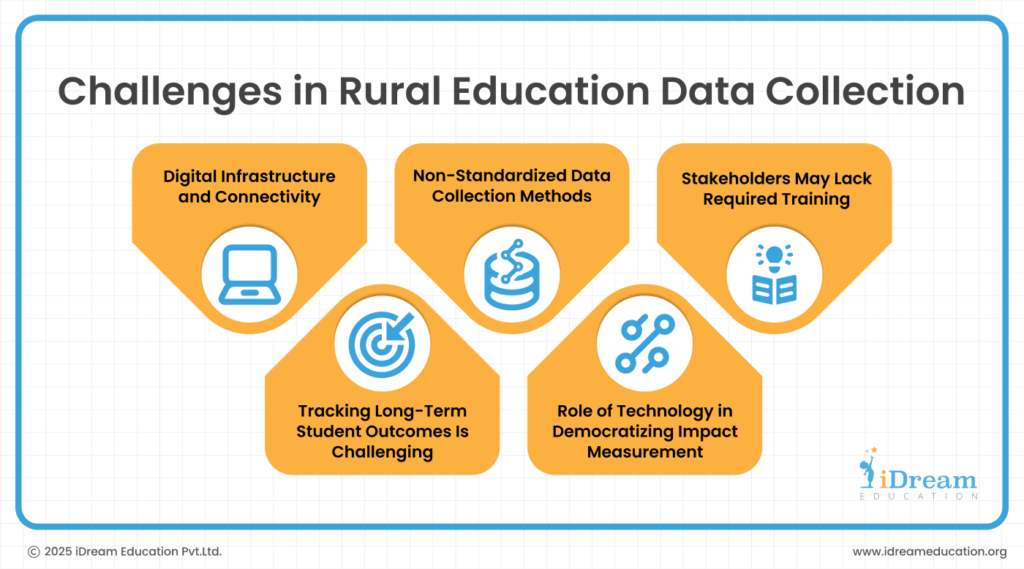
To measure CSR initiative impact, reliable data isn’t just helpful—it’s essential. Here’s what makes collecting that data in rural areas so tough:
1. Digital Infrastructure and Connectivity
Spotty internet access makes real-time data collection and transmission nearly impossible in many areas.
2. Non-Standardised Data Collection Methods
When different organisations use different measurement techniques for their CSR programmes, it may result in inconsistencies that make school-to-school comparisons difficult.
3. Stakeholders May Lack Required Training
Teachers, parents, and administrators—especially in rural regions—often do not have adequate training. This can result in inaccurate reporting of student progress and infrastructure needs.
4. Tracking Long-Term Student Outcomes Is Challenging
Tracking the long-term impact of education CSR initiatives is difficult as rural students often drop out or migrate for work.
5. Role of Technology in Democratising Impact Measurement
Data analytics can help evaluate large datasets to pinpoint education trends, predict dropout risks, and suggest targeted interventions. Readily available data is essential for effective technology adoption, which is often a challenge in rural setups.
Digital learning platforms help track student engagement, progress, and learning effectiveness. Solutions like iDream Education’s tablet-based and offline-friendly digital learning platforms help bridge this gap by enabling real-time tracking of student engagement, progress, and learning outcomes.
Integrating ESG and CSR in Education
CSR initiatives that combine Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into their approach are more effective and yield long-term positive impacts.
Integrating ESG criteria with traditional CSR approaches can help transform education in the following ways:
Environmental Initiatives
Using eco-friendly practices, such as cutting waste and using resources wisely within schools, can greatly lower environmental impact. These operational changes establish a foundation for institutional sustainability while modelling responsible stewardship.
Many universities are integrating ESG into their curricula, particularly in business and management programmes.
Adding topics like climate change, protecting biodiversity, and managing resources sustainably to teaching plans builds environmental responsibility in students. This integration ensures that environmental awareness becomes embedded within educational outcomes rather than merely as supplementary knowledge.
Social Initiatives
Studies suggest that CSR-driven educational programmes that actively involve parents, local authorities, and charities ensure sustainability and relevance to community needs. Through this approach, educational institutions can better understand and address specific local challenges.
In fact, European business schools are increasingly integrating sustainability into their curricula.
Providing access to digital learning tools and modern educational facilities helps address gaps in education, especially in underserved communities. These technological interventions serve to democratise learning opportunities.
| Read More: The Intersection of Digital Education and ESG: Building a Sustainable and Inclusive Future |
Governance Initiatives
Ensuring that education programmes follow ethical standards, protect student data, and promote fair learning opportunities demonstrates strong governance principles. These practices establish trust among stakeholders whilst safeguarding the integrity of educational systems.
Studies note that aligning CSR initiatives with ESG goals improves transparency and accountability, leading to more effective and sustainable educational outcomes. This strategic alignment enables institutions to measure progress systematically and adjust approaches based on evidence rather than conjecture.
Measuring and Reporting on ESG Components
Evaluating the ESG components within the education programmes is done through:
- Establishing clear ESG objectives that align with educational initiatives.
- Defining quantifiable metrics to measure student diversity, track resource consumption, and the impact of educational programmes.
- Adopt a collaborative approach to evaluate ESG initiatives to ensure they meet stakeholder needs and expectations.
- Have a transparent approach to reporting.
- Commit to continuous improvement through periodic assessment of ESG performance.
Example
Samsung runs an ESG-aligned education initiative: “Solve for Tomorrow“. This global initiative programme empowers young students with STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education to help them solve real-world sustainability challenges.
The initiative is also instrumental in providing students of underserved and diverse backgrounds access to quality STEM education.
3 Impact Parameters of CSR Programmes in Education
Let us focus on a few core impact parameters to gauge the effectiveness of their CSR initiatives:
1. Learning Outcome Metrics
Student improvement in knowledge, critical thinking, and problem-solving can be measured through:
- Grades and graduation rates (academic performance)
- Skill development indicators like communication, technical abilities, and leadership growth
- Participants in workshops indicate student engagement level.
2. Infrastructure Utilisation Metrics
To evaluate infrastructure usage:
- Track the frequency of online course usage, completion rate of modules, and login numbers to help measure digital resource adoption rates.
- Evaluate smart classroom usage patterns through the frequency of classroom sessions and student participation.
- Monitor device accessibility statistics, like student-to-device ratio and maintenance requirements.
3. Teacher Empowerment Indicators
These are indicators to assess the programme’s effectiveness in improving teachers’ skills and confidence through:
- Estimating the number of teachers trained and certifications obtained helps track their professional development.
- Activity-based learning adoption is an effective indicator for assessing enhancement in teaching methodology.
- Digital Tool Adoption Rate is measured by estimating the number of schools using digital teaching aids and the frequency of use of audio-visual tools.
CSR Programmes: Data Collection Framework
A well-designed data collection framework helps gauge if the CSR programmes are having any meaningful and desired impact. Here is how organisations can create a robust data collection framework:
1. Adopt a Systematic Approach to Gathering Data
A structured data collection process aligned with CSR goals defines data collection frequency, combines qualitative and quantitative data, and ensures data reliability is crucial for effective implementation.
2. Integrate Offline and Online Data Collection Methods
Have mechanisms to ensure seamless data gathering for both tech-savvy and underprivileged schools.
Combining paper-based surveys, on-ground teams, and digital learning platform trackers with teacher dashboards provides meaningful insights.
3. Use Cloud-Based Monitoring Systems
Cloud-based systems offer real-time data collection, scalability, and security and use AI and data analytics to get valuable insights.
4. Rely on Real-Time Reporting Mechanisms
Real-time reporting enhances decision-making based on data and minimises delays. Notifications for critical issues, such as low student participation, provide actionable insights.
5. Build Sustainable Data Collection Processes
Training local teachers, automating data gathering, and partnering with local authorities go a long way in ensuring the sustainability of CSR and data collection initiatives.
Drawing Insights from Collected Data To Boost the Impact of Education CSR Programmes
Conclusions drawn from data analysis help maximise CSR impact in the following ways:
1. Converting Raw Data into Actionable Insights
Data analysis helps draw actionable insights from unstructured data and offers meaningful takeaways by identifying trends.
2. Correlation vs. Causation in Education Impact
The focus should be on addressing the root causes of issues. For example, an improvement in students’ performance using digital platforms cannot lead to a direct conclusion: the progress is due to the use of technology solely.
3. Creating Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
A mechanism that offers data-driven insights and continuously refines CSR initiatives ensures that any gaps are identified and resolved immediately.
4. Using Data Visualisation for Stakeholder Communication
Dashboards and infographics are instrumental in presenting complex data in an easy-to-understand and compelling format for stakeholders.
Real-World Impact: CIPLA Foundation Implementation Case Study
Data-driven approaches in education CSR can create a measurable, sustainable impact in education, particularly for underserved rural communities.
Let’s take an example of the CIPLA Foundation’s successful digital learning initiative implemented across Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Madhya Pradesh.
The Challenge
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed a critical gap in rural education.
- When schools closed during lockdowns, many students lacked access to digital devices, relevant e-learning resources, and reliable internet connectivity.
- Even after the pandemic subsided, maintaining digital learning momentum and improving educational outcomes remained significant challenges.
The Solution: A Comprehensive Digital Learning Ecosystem
In partnership with iDream Education and other stakeholders, the CIPLA Foundation implemented contextual digital learning solutions across 116 schools, reaching over 6,000 students:
- Personalised Learning Devices: Android tablets with SD cards preloaded with state board-aligned digital content
- Shared Infrastructure: iPrep Digital Libraries with Android tablets and charging racks
- Classroom Enhancement: iPrep Smart Classes with plug-and-play functionality
- Linguistic Inclusivity: Bilingual learning platform supporting both English and local languages
- Data-Driven Monitoring: Centralised reporting dashboard for continuous tracking
- Teacher Empowerment: Ongoing capacity building programmes for educators
Measurable Outcomes
The initiative’s impact was precisely measured through comprehensive data tracking over three years (2021-2024):
| Resource Type | Usage Metrics | Region |
| Tablets | 31,000+ hours | Maharashtra |
| Digital Library | 13,000+ hours | Karnataka & MP |
| Smart Class | 8,000+ hours | Maharashtra |
| Grade 10 Tablets | 4,300+ hours total (4,000+ in Maths) | Karnataka |
Student engagement patterns were also quantified, with learners typically spending 45 minutes to 1 hour per day on tablets at home for 15-20 days each month.
What Were the Key Success Factors?
- Contextual Solution Design: Technologies adapted to specific regional and school needs
- Bilingual Approach: Content availability in both English and local languages ensured accessibility
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time data collection enabled ongoing optimisation
- Teacher Training: Sustained capacity building ensured effective implementation
- Home-School Integration: Learning continued seamlessly between classroom and home environments
Implications for Education CSR Strategy
The CIPLA Foundation case study exemplifies several best practices for data-driven education CSR:
- Addressing Root Causes: Rather than simply donating technology, the programme tackled fundamental access and engagement issues
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Usage metrics provided clear evidence of impact
- Contextual Adaptation: Solutions varied by region based on specific needs
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Partnership between corporate foundation, EdTech provider, and local institutions
- Long-Term Commitment: Sustained three-year implementation allowed for continuous improvement
5 Tips to Implement Data-Driven Approaches
CSR departments can adopt the following tips to implement projects via data-driven approaches:
1. Define Objectives & Track Impact
Set clear goals and measurable KPIs to assess education CSR initiatives effectively.
2. Leverage Technology & Data Analytics
Use AI, Big Data, and digital platforms to collect, analyse, and track real-time education outcomes.
3. Engage Stakeholders & Ensure Collaboration
Work with schools, government bodies, and NGOs to align efforts and enhance impact measurement.
4. Adopt a Hybrid Data Collection Framework
Combine offline surveys with online dashboards for comprehensive and scalable data gathering.
5. Optimise & Report Findings
Use data insights to refine CSR strategies and ensure transparent impact reporting.
Data-driven Approaches: 5 Essential Tools and Technologies
Here are some tools and technologies that may come in handy:
- AI & Data Analytics Platforms: Use tools like iPrep to consistently analyse student performance and track the impact of the programmes.
- Cloud-Based Monitoring Systems: AWS, Google Cloud, and local edtech platforms offer scalable data storage and security.
- Mobile Learning Solutions: As a learning super app with offline access, iPrep enables digital education in remote areas.
- Survey & Feedback Tools: Platforms like SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, and KoboToolbox assist in data collection and analysis.
- Government Databases & Dashboards: DIKSHA, UDISE+, and state education portals provide critical educational statistics and insights.
Final Note
CSR in education has facilitated last-mile connectivity and made education accessible to all. Data-driven modern approaches focus more on evaluating the long-term impact of education.
Cutting-edge technology helps improve education delivery, empowers stakeholders, adds joy to learning, and offers a more functional view of the effects education has on communities.
Through the iPrep platform, iDream Education delivers a comprehensive impact measurement system designed to support data-driven educational CSR initiatives. By empowering teachers and students in schools and at home, iPrep facilitates universal access to learning and growth.
If you are looking for an all-in-one and impactful digital learning solution, we have the perfect solution for you.
Check out our offerings in detail.