The Transformative Potential of Ed Tech in Shaping Positive Learning Behaviour

A child glued to a smartphone is a common sight today. Parents and educators frequently express concern over the time children devote to smartphones, hoping for a similar enthusiasm for academic studies. The challenge, however, lies not in the child’s “misplaced” attention but in the perceived disconnect between classroom and after-school virtual activities. Imagine the possibilities if these realms converged—leveraging technology’s strengths to foster positive learning behaviour in students to achieve academic excellence as well as holistic growth.
In recent years, the advantages of Educational Technology in democratizing access to quality education have gained fair recognition. However, Ed Tech’s potential to induce positive learning behaviour is an aspect yet to be thoroughly explored. This emerging dimension has the capacity to bring about a paradigmatic shift in the learning experience and achieve positive learning outcomes.
The Significance of Technology-infused Learning Experiences
Many young individuals, often perceived as disinterested in traditional school settings, exhibit remarkable dedication to learning beyond school hours. After school activities encompassing the Internet, YouTube, games, and smartphones, serve as a vibrant space where students teach themselves practical insights about their current realities.
Contrary to stereotypes, students today do not inherently possess short attention spans. Rather, they manifest a refined ability to concentrate, particularly when captivated by movies, videos or games. The shifting style of attention does not reflect diminished capabilities. It is an adaptation to a world saturated with diverse stimuli wherein students have learned to prioritize what resonates with their individual interests. In an era marked by overstimulation, the ability to choose, personalize, and individualize learning experiences has become a necessity.
Unfortunately, traditional teaching methods often fall short of meeting these evolving needs. The absence of technology integration in schools accentuates this disconnection, as students’ technology-rich lives outside the classroom diverge sharply from the learning environment in school. To bridge this gap, education must evolve to offer technology-infused learning experiences, acknowledging the changing dynamics of student engagement and motivation.
Intrinsic Motivation: EdTech and Student Engagement
With Ed Tech becoming essential to modern education, experts have turned to behavioural psychology to gain deeper understanding. These efforts have yielded encouraging results on the correlation between Ed Tech and positive learning behaviour.
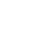
When viewed through the lens of the self-determination theory (SDT), educational technology emerges as a potent force for fostering positive learning behaviour in students. SDT holds that individuals are more likely to be intrinsically motivated when their psychological needs for autonomy, relatedness and feelings of competence are satisfied.
Tech-Empowered Autonomy and Student Engagement
The Autonomous Learner Model (ALM), conceived by George Betts and Jolene Kercher, is a framework to foster independent and self-directed learning in students. The model is rooted in the belief that autonomy and self-directed exploration enhance motivation, sparking a genuine interest in subjects.
Digital education empowers autonomy in student learning by providing personalized and self-directed educational experiences. Digital tools offer a diverse range of resources, allowing students to explore topics aligned with their interests and pace. Interactive platforms, and adaptive technologies enable students to set goals, choose study methods, and progress at their unique pace. This fosters a sense of ownership, as students choose and navigate their educational journeys independently. Moreover, technology facilitates anytime, anywhere learning, giving students the flexibility to engage with educational content beyond traditional classroom settings. Through digital tools, students assume greater responsibility for their learning, promoting self-directed exploration.
Meeting Relatedness Needs: Collaboration in Digital Education
Self-determination theory also underscores the vital role of the social context in learning and its impact on learning behaviour. However, scepticism among educators regarding the effectiveness of online learning remains, with concerns about rigour and learning outcomes.
Yet, studies have shown that when digital education incorporates collaborative features such as discussion forums it can be effective in meeting the relatedness needs of students. Online learning communities, facilitating collaborative, task-driven, and socio-emotional interactions, play an important role in enhancing a sense of security and satisfaction among learners.
The Role of Interactive Learning in Student Mastery and Competence
Interactive tools and adaptive platforms engage learners in tasks that match their abilities, fostering a sense of efficacy. By tailoring content to individual skill levels, technology ensures that students are appropriately challenged. Real-time feedback provides constructive insights, reinforces achievements, and guides improvements, and contributes to overall competence. Students thus develop a sense of mastery of the topic being studied and feel positively reinforced. This leads to better behavioural and emotional engagement with the learning process.
Case Studies on Classroom Tech Integration
The exploration of the implications of technology-integrated learning in classrooms have prompted experts to engage in meaningful on-field experiments. A notable example is a study conducted in Greece, involving 30 students aged 11 to 16 from a private foreign language institute in 2019–2020. The participants were split into two groups – one taught with Gamified English Teaching (GET) technology and the other through traditional methods. The GET group, utilizing an interactive whiteboard and student response system, exhibited increased academic well-being over time. However, the traditional group showed no significant change. This study emphasizes a positive correlation between classroom technology and enhanced academic performance.
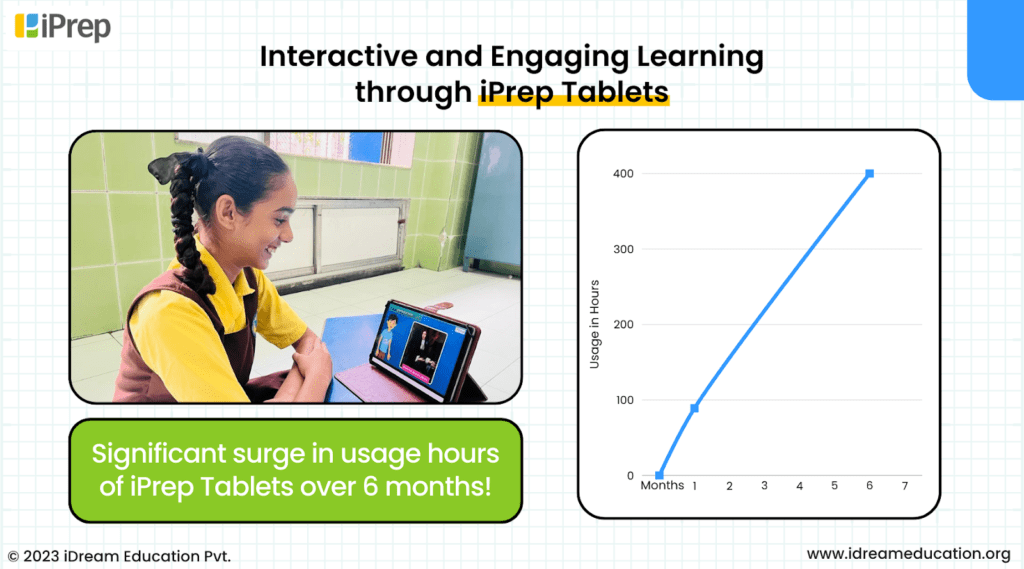
Similarly, in India, the integration of technology into classrooms has demonstrated promising trends and outcomes. Under the Leap to Shine project (2023), students at the SPRJK Trust School in Ghatkopar, Mumbai, were provided with iPrep Tablets. This is an innovative digital learning solution featuring engaging and interactive content across grades to facilitate holistic learning. Within six months, the average tablet usage hours increased from an initial 89 hours to approximately 400 hours. This exhibited a positive trend in student engagement. Students in 9th and 10th grades showed heightened involvement with subjects like Math and Science. They especially preferred interactive content categories such as videos and intuitive practice tests.
To Conclude
The above discussion highlights the inevitable integration of technology into classrooms for comprehensive and meaningful learning. The distinction between the classroom and the technology-infused reality outside is diminishing. This emphasizes the need to view technology as an enabler rather than a hindrance.
Today, children experience many novel tech-infused stimuli. It is crucial to recognize that these have become integral to their real-world experiences, shaping their learning behavior. Failing to meaningfully integrate digital tools in education would be a disservice, hindering our students’ preparedness for the future. Hence, the shift towards personalized and collaborative learning experiences powered by educational technology becomes increasingly evident.
The integration of technology in education has the potential to revolutionize learning.
In case you would like to know more about iPrep by iDream Education, visit our website, www.idreameducation.org, or write to us at share@idreameducation.org