Empowering India’s Multilingual Landscape: Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Bilingual Education

Examining the role and significance of bilingual education in the country, India’s National Education Policy 2020 adopted a multilingual approach to education where the medium of instruction in schools till Class 5 mandatorily, (but preferably till Class 8 and beyond) will be the regional language of students. With this approach, the NEP 2020 aims to preserve linguistic diversity and enhance students’ learning levels in Indian schools.
Bilingual Education in schools gives students the opportunity to better comprehend, retain, and understand information. Delivering educational content in a familiar language reduces cognitive load, enabling students to focus on the content without language barriers
Apart from that, when learners have the option to switch to a different language, such as English or Hindi, not only does it enhance their understanding of the educational content but also improves their English language skills and learning & retention.
In light of this, the NEP 2020 advocates a three-language formula in Indian schools. This includes incorporating the regional language, English, and another modern Indian language into the school curriculum, thereby enhancing students’ linguistic proficiency and encouraging bilingual education.
Advantages of Bilingual Education in India

- Preserving Cultural and Linguistic Diversity
Over 19,500 different languages and dialects are spoken in India, making it a linguistically diverse nation.
Bilingual education contributes to the preservation and promotion of the rich cultural and linguistic heritage of various communities.
Empowering children to learn and value their native language alongside widely spoken ones like Hindi or English is essential.
This promotes a sense of belonging and cultural identity pride.
- Enhancement of Cognitive and Foundational Skills
Research has consistently demonstrated the cognitive benefits of bilingualism.
It improves cognitive adaptability, problem-solving skills, and originality.
Bilingual students typically have superior attention control, multitasking skills, and memory.
Additionally, they tend to perform better on standardized tests of math, reading, and vocabulary and develop better Foundational Learning and Literacy (FLN) skills.
- Enhanced Accessibility to Opportunities
Bilingual education equips students with the language skills necessary for global competition, due to improved English Language Learning and its understanding & application.
Facilitating access to diverse academic resources, international collaborations, and careers requiring English proficiency broadens opportunities for students.
Challenges in Implementing Bilingual Education in India
The implementation of bilingual education in India presents several significant obstacles. Here are three key points supporting this assertion:
Challenge 1: Diverse linguistic environment
India is a tremendously diverse nation with numerous languages spoken throughout its regions.
According to the 2001 Census, India is home to 122 major languages and 1599 additional languages.
This linguistic diversity makes it difficult to prioritize which languages should be taught in bilingual education.
In addition, many communities speak dialects or languages for which there are no standardized educational materials, making it difficult to create a curriculum that is inclusive of all linguistic groups.
Challenge 2: Absence of Standardized Curriculum Materials
Creating a standard curriculum and educational materials for bilingual education is a daunting task.
It necessitates the creation of multilingual textbooks, instructional materials, and assessments.
This necessitates not only a substantial financial investment but also a dedicated effort to ensure the quality and cultural relevance of these materials.
Additionally, training teachers proficiently in multiple languages and methodologies specific to bilingual education is a substantial challenge.
Challenge 3: Infrastructure and Access Disparities
India faces significant infrastructure and access disparities, especially in rural and remote regions.
Providing bilingual education requires not only the creation of appropriate curricula and materials but also the provision of adequate physical and technological resources in schools.
This includes access to well-equipped classrooms, libraries, and instructional technology. Closing these infrastructure gaps is a crucial obstacle in India’s implementation of bilingual education.
Incorporating Technology to Solve Challenges in Bilingual Learning
- Digital Learning Platforms for Customized Curriculum
By leveraging technology, digital learning platforms with a more personalized and adaptable curriculum can be introduced in schools where students face diverse educational content needs.
One such name in the digital learning platform is iPrep by iDream Education.
This multilingual learning platform contains rich and comprehensive digital content for classes K-12.
Such platforms can dynamically adapt to each student’s linguistic background and learning pace.
- Multimedia Resources to Bridge Resource Gaps
The lack of standardized curriculum and resources can be overcome with the help of technology.
It is possible to create open-access e-learning resources with a wealth of educational materials in multiple languages.
This includes e-books, interactive multimedia content, and educational applications.
The iPrep digital learning app is a combination of the above. The digital learning platform includes animated lessons, practice with instant feedback, practicals, digital syllabus books, notes, and assessments with exam preparation.
Beyond academics, it offers a rich book library with books on personal growth, stories and picture books, inspiring biographies, and interactive lessons for holistic learning and growth.
- Digital learning Devices to improve Infrastructure Disparities
Digital learning devices and technologies such as smart ICT Labs with tablets and Smart Classrooms can significantly enhance educational infrastructure.
Students have access to an abundance of digital resources, interactive learning materials, and multimedia content via these tools.
They can bridge the infrastructure gap by creating a more conducive learning environment, particularly in regions where traditional infrastructure may be insufficient or lacking.
This method not only improves the quality of education but also prepares students for a future dominated by technology.
Real-life Implementation of Digitally Enhanced Bilingual Education in Indian Schools
In a rural government school in Sangvi Telangana young minds determined to learn faced the challenge of good education resources available in their native language i.e. Telugu.
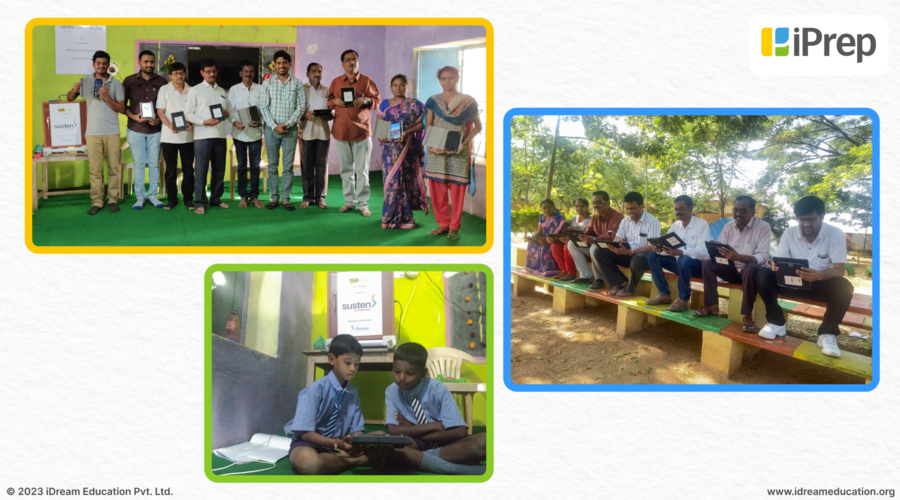

Also, the school lacked the basic infrastructure required to create an appropriate learning environment for students.
Educators who had exhausted every traditional education medium to find a solution to the above problems now turned to infrastructure-light digital learning solutions.
With a coordinated effort by Mahindra Susten and iDream Education, iPrep Digital Library which was preloaded with enjoyable and curriculum-aligned rich digital content in both English and Telugu for classes 1st to 8th was provided to the school.
The students and teachers were delighted with the quality of the e-learning content such as animated video lessons, e-books, audiobooks, etc. present on the tablets.
They could easily switch from one class to another with multigrade access and from one language medium to another with multilingual access.
This joint initiative helped enhance the learning outcomes of over 100+ students in Sangvi, Telangana setting a positive example for digitally enhanced bilingual education in Indian schools.
Recommendations for Stakeholders: A Roadmap for Digitally Enhanced Bilingual Education in India
Here are some suggested recommendations for stakeholders such as NGOs and CSRs towards the implementation of digitally advanced bilingual education in Indian schools:
- Investment in Digital Infrastructure-
Allocate funds for procuring tablet-based ICT Labs with preloaded bilingual content to boost learning in schools emphasizing regional languages.
- Curriculum Alignment and Enrichment-
In collaboration with digital learning content providers, ensure that the digital resources are aligned with the state curriculum framework and enriched with engaging multimedia content.
- Teacher Training and Capacity Building-
Conducting comprehensive training programs for teachers will help them effectively integrate digital resources into their teaching methods, ensuring they can maximize the benefits of bilingual education while being able to complete their curriculum requirements.
- Public-Private Partnerships-
Encourage collaborations between government bodies, private organizations, and NGOs to leverage resources, expertise, and technology for the widespread implementation of digitally enhanced bilingual education in Indian schools.
Conclusion:
Bilingual education in India’s diverse linguistic landscape, with 19,500+ languages, is crucial for enhancing students’ academic success.
Utilizing technology can bridge gaps for students fluent in their native language but lacking resources for academic advancement.
Using multilingual ICT Labs with regional languages can revolutionize learning, boost English proficiency, and preserve cultural diversity in education