Elevating Cognitive Learning Levels with Bloom’s Taxonomy in Digital Education

Fostering cognitive growth with Bloom’s Taxonomy framework is paramount for preparing students not only to learn effectively but also to thrive in any educational landscape. According to Oxford Learning, “Cognitive learning helps students learn effectively and ensures that the concepts learned are understood, instead of being temporarily memorized.“
When it comes to Bloom’s Taxonomy, it is the core of many teaching philosophies and some very well-regarded education material. It is a well-known and reputed framework that categorizes educational objectives into six distinct cognitive levels of learning to help educators build better learning environments for students.
These levels, ranging from basic recall of information to advanced critical thinking and creation, serve as a guiding light for educators in designing effective learning experiences to increase student learning levels.
In the digital age, where technology is seamlessly integrated with education, leveraging models such as Bloom’s Taxonomy to enhance the level of cognitive learning in learners is imperative.
The synergy of digital education and Bloom’s taxonomy not only enhances the quality of instruction given by educators but also empowers students with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in today’s information-driven society.
This article explores the pivotal role of educators in harnessing the potential of Bloom’s Taxonomy in integration with digital learning tools, leading students toward higher levels of cognitive learning.
What is Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a framework introduced by the visionary educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom back in 1950. This taxonomy initially outlined six distinct cognitive levels: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
However, in 2001, recognizing the need to align with 21st-century learning models, significant adjustments were made. The focus shifted from static nouns to dynamic, action-oriented verbs. Additionally, the top two stages were reorganized, reflecting a more fluid progression of cognitive development. This evolution met with the need for an adaptable framework that could meet the evolving challenges of modern education.
Significance of Bloom’s Taxonomy in Education
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a widely used tool that informs and elevates the teaching process. It provides a structured approach to crafting learning experiences that cater to the diverse needs and abilities of students.
By categorizing learning objectives into distinct cognitive levels, educators can effectively frame instruction and ensure that students engage with content at appropriate levels of complexity. This targeted approach enhances comprehension and retention, ultimately leading to more meaningful and lasting learning outcomes.
Here’s a closer look at why Bloom’s Taxonomy holds such profound significance in elevating the cognitive levels of learning in students:

- Clarity in Learning Objectives: Bloom’s Taxonomy provides educators with a structured framework for setting clear and measurable learning objectives. This clarity is essential for designing curriculum and instructional materials that align with desired outcomes.
- Enhancing Critical Thinking: Fostering critical thinking skills is paramount for students. Bloom’s Taxonomy places a spotlight on these skills, encouraging educators to develop lessons that challenge students to think critically, analyze information, and make informed decisions.

- Personalized Instruction: Recognizing that students progress at different rates and have diverse learning needs, educators can use the taxonomy to tailor instruction. It offers a range of cognitive levels, allowing educators to provide differentiated learning experiences.
- Effective Assessment: Bloom’s Taxonomy guides the creation of assessments that accurately gauge student progress. By aligning assessments with the cognitive skills students are expected to demonstrate, educators can assess learning effectively.

- Engagement and Motivation: Educators understand the importance of keeping students engaged and motivated. The taxonomy offers a variety of cognitive levels, enabling educators to design lessons that cater to different learning styles and preferences.
- Encouraging Creativity and Innovation: In the pursuit of nurturing well-rounded individuals, Bloom’s Taxonomy encourages educators to incorporate activities that promote creativity and innovation. This includes tasks that require students to generate original ideas and solutions.

- Effective Collaboration: Educators work together to provide the best possible education for their students. Bloom’s Taxonomy provides a common language for discussing learning objectives and instructional strategies, fostering collaboration among teaching teams.
- Empowering Student Ownership: The taxonomy can also empower students. Educators can guide students in setting their own learning goals and understanding where they stand in terms of cognitive development. This fosters a sense of responsibility for their education.

- Adaptability to Changing Times: As education evolves, Bloom’s Taxonomy remains relevant. It can be applied in traditional classrooms as well as in digital and blended learning environments, making it a versatile tool for educators.
- Lifelong Learning Skills: By focusing on higher-order thinking skills, Bloom’s Taxonomy equips students with skills that extend beyond the classroom. These skills are essential for lifelong learning and success in various academic and professional settings.
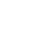
6 Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy: The new and old versions explained
The concept of Bloom’s Taxonomy envisions learning as a ladder, with foundational knowledge at the bottom and more profound understanding and application at the top.
The Six levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy- explained as per the revised model with examples:
Level one- Remembering
In the first level of Bloom’s Taxonomy learners recall the basic facts. Example- “What is photosynthesis?” Answer: “Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy to produce food.”
Level two- Understanding
The second stage deals with explaining the concept. Example- “How does photosynthesis work?” Answer: “Photosynthesis involves the absorption of sunlight by chlorophyll, which is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.”
Level three- Applying
For the third level, learners should use the knowledge they accrued practically. Example- “If you were given a scenario with specific environmental conditions, predict how it might impact the rate of photosynthesis in plants.”
Level four- Analyzing
Breaking down information and analyzing it happens in the fourth stage of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Example- “Examine the different stages of photosynthesis and explain the role of each stage in the overall process.”
Level five- Evaluating
In the fifth level, students have to make a judgment call. Example-“Assess the importance of photosynthesis to the ecosystem and consider the potential consequences if this process were to be disrupted.”
Level six- Creating
For the last level, students generate new ideas or solutions. Example- “Devise an experiment to improve the efficiency of photosynthesis in plants under controlled conditions, considering variables like light intensity or temperature.”
Bloom’s Taxonomy underwent a significant evolution from its original version in 1950 to the revised version in 2001. The newer iteration focused on a more dynamic and action-oriented approach, reflecting the changing demands of modern education. This shift emphasized the importance of adaptability and relevance in guiding effective teaching and learning practices.
| Original Bloom’s Taxonomy (1950) | Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy (2001) |
| Introduced by Benjamin Bloom in 1950. | Updated in 2001 to align with modern learning models. |
| Outlined six cognitive levels: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. | Emphasized dynamic, action-oriented verbs to describe cognitive processes. |
| Used static nouns to describe cognitive processes. | Reorganized the top two stages for a more fluid cognitive progression. |
| Represented a foundational framework for educational objectives and assessment. | Recognized the evolving educational landscape and adapted to meet 21st-century learning needs. |
The Integration of Bloom’s Taxonomy in Digital Education
The integration of Bloom’s Taxonomy into digital education stands as a beacon of pedagogical innovation in the educational landscape. This harmonious fusion of a time-honored cognitive framework with the dynamic capabilities of digital education has ushered us into a new era of enriched learning experiences.
Digital platforms and tools provide a dynamic and flexible environment for educators to implement Bloom’s Taxonomy effectively. They offer a plethora of resources, assessment options, and interactive elements that cater to diverse cognitive levels.
By leveraging these technologies, educators can create engaging learning experiences that nurture critical thinking, problem-solving, and higher-order cognitive skills in students.
Here’s a breakdown of how digital education tools can be instrumental in enhancing the Cognitive Learning Levels of students:
Access to a Diverse Range of Learning Resources–
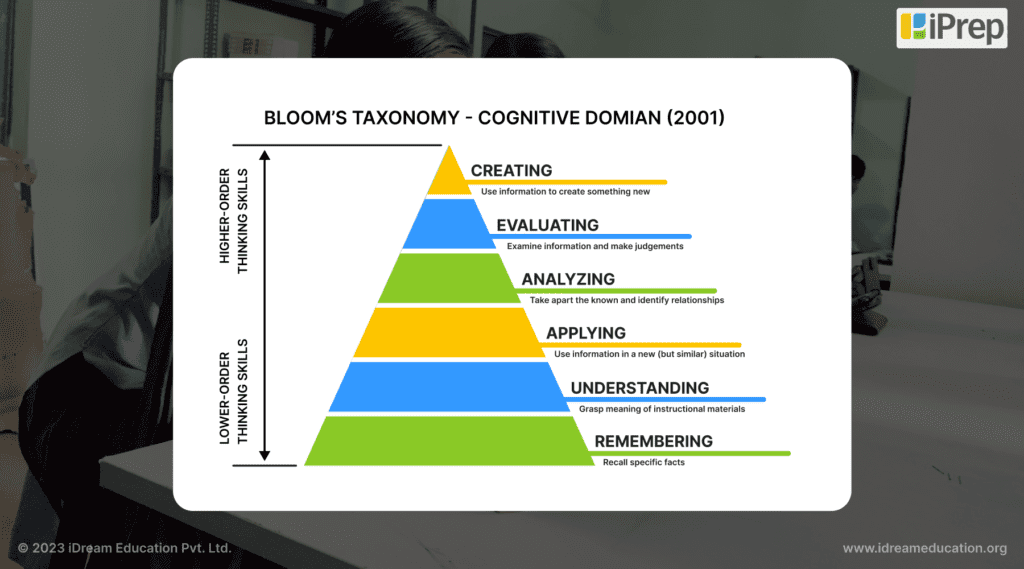
Digital Education platforms such as iPrep by iDream Education (the platform also uses Bloom’s Taxonomy for its learning content development) provide a vast array of multimedia resources, including animated video lessons, practice tests, e-books, audiobooks, and more. This abundance allows educators to cater to various cognitive levels, from basic understanding to advanced analysis and application.
Recently, iDream Education in partnership with the Saint Gobain Foundation, implemented iPrep Digital Library, a tablet-based smart ICT lab setup integrated with iPrep’s content to engage and educate students even in the absence of teachers.
Under this initiative Parul Tundwal, Principal at Government Senior Secondary School, Bhaiwadi, Rajasthan stated that the iPrep Digital Tablets containing detailed NCERT syllabus for classes K-12 for all subjects enabled quality and joyful learning among the students. The nano-animated video content for all the lessons covered in the syllabus is highly interactive and loved by students at all grade levels.
The assessment questions based on the video lessons help students have a complete understanding of the taught content and also help teachers understand the cognitive learning level of each student.
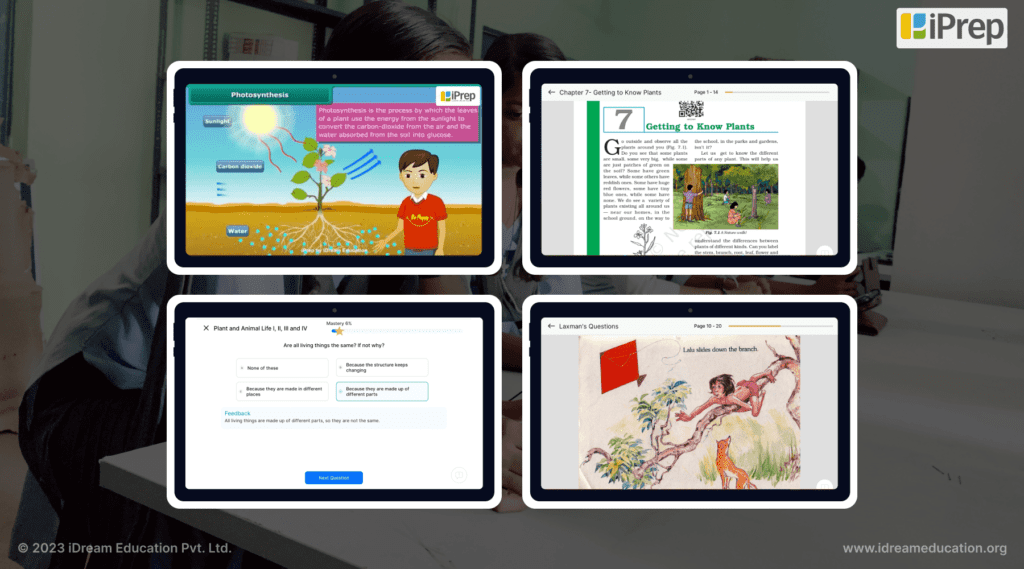
Adaptive Learning Technologies for Personalization–
Adaptive learning platforms such as iPrep PAL based on the EdTech Tulna framework for Personalised Adaptive Learning give students a diagnostic test for every chapter in K-12 learning. This test is divided into 4 Levels, each presenting 12 questions for the learner to answer based on the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy model.
After taking the diagnostic assessment, PAL’s data analytics assesses a student’s current level and dynamically determines a personalized learning path with practice questions and remedial video lessons. This ensures that each student is appropriately challenged, facilitating growth in cognitive skills and covering learning gaps.
After having gained mastery over chapter levels in practice sessions of their grade level, students take a final test. The percentage performance of a student in the earlier Diagnostic Test and this Final Test can be analyzed in the reporting dashboard of iPrep PAL. This way, students, teachers, parents, and other stakeholders can measure the improvement level of the student.
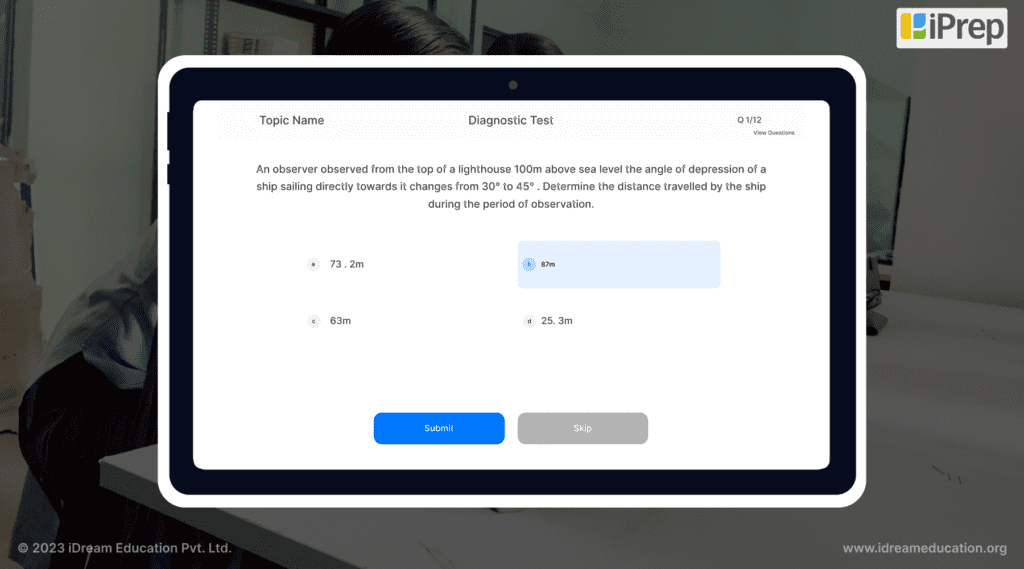
Gamification and Interactive Learning Modules: Gamified elements within digital platforms can be designed to encourage problem-solving, decision-making, and strategic thinking. These elements naturally align with the higher-order cognitive skills outlined in Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Conclusion:
The seamless integration of Bloom’s Taxonomy in the dynamic landscape of digital education demonstrates the transformative power of pedagogy. Educators blend proven cognitive frameworks with digital platforms for a new era of enriched learning experiences and dynamic capabilities. This synthesis fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and higher-order cognitive skills, preparing students for an increasingly complex world.
Digital tools like iPrep offer educators abundant resources for personalized learning, accommodating diverse cognitive abilities and integrating Bloom’s Taxonomy. The integration of iPrep PAL’s adaptive learning tech ensures tailored challenges, fostering robust cognitive development for every student.
Bloom’s Taxonomy and digital education will continue to shape the future of learning as we move forward. Together, they equip students not only to succeed in their academic endeavors but also to thrive in a world characterized by constant innovation and complexity. We embark on a journey towards a more enlightened and empowered generation of learners through this harmonious integration.
If you would like to know more about our digital learning solutions, comment below or write to us at share@idreameducation.org